The Power of Artificial Intelligence: The Ultimate Game-Changer
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a discipline of computer science that tries to construct robots or systems that can do tasks that would normally need human intelligence. These tasks include learning from experience, recognizing patterns, making decisions, understanding natural language, and solving complex problems.
AI systems are built to analyze massive volumes of data, spot patterns, and make predictions or suggestions based on that data. They use algorithms and mathematical models to process information, learn from it, and improve their performance over time.
There are various types of AI, such as Narrow AI, which is designed for a specific task, like language translation or playing chess, and General AI, which would possess human-like intelligence and the capacity to carry out a variety of jobs.
AI has numerous applications across various industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, manufacturing, and entertainment. It has the potential to revolutionize the way we live and work, but it also raises ethical and societal concerns that need to be carefully addressed.
In summary, artificial intelligence is a rapidly advancing field of computer science that seeks to develop intelligent machines capable of emulating human cognitive abilities and performing tasks with efficiency and accuracy.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be categorized into three main types based on their capabilities:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): Narrow AI refers to AI systems that are designed and trained for a specific task or a narrow set of tasks. These systems excel in performing predefined functions and are not capable of generalizing their knowledge to other domains. Examples of Narrow AI include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, image recognition systems, and recommendation algorithms used by streaming platforms.
- General AI (Strong AI): General AI, also known as Strong AI, is an advanced form of AI that aims to possess human-like intelligence and capabilities. Unlike Narrow AI, General AI would have the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, just like humans. Achieving General AI is still a theoretical goal and remains a subject of ongoing research and development.
- Artificial Superintelligence (ASI): Artificial Superintelligence refers to an AI system that surpasses human intelligence in almost all areas, including creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making. This type of AI is purely speculative at present, and its potential impact on society and humanity raises significant ethical and existential questions.
It’s important to note that while Narrow AI is currently prevalent and has numerous real-world applications, the development of General AI and Artificial Superintelligence is still a long-term goal and involves complex technical, ethical, and philosophical challenges. As of now, most AI systems fall under the category of Narrow AI, serving specific purposes and domains.

Artificial intelligence (AI) has several applications in a variety of sectors and fields. Some of the most important applications of AI are:
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI-powered NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language. It is used in chatbots, sentiment analysis, language translation, and virtual assistants.
2. Machine Learning: AI algorithms in machine learning can analyze vast amounts of data to make predictions, recognize patterns, and detect anomalies. Predictive maintenance, recommendation systems, and fraud detection are some examples of applications.
3. Computer Vision: AI enables machines to interpret and understand visual information from images and videos. Computer vision is used in facial recognition, object detection, autonomous vehicles, and medical imaging analysis.
4. Speech Recognition: AI-powered speech recognition systems convert spoken language into written text. They are used in voice assistants, transcription services, and call center automation.
5. Autonomous Systems: AI is crucial for developing autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars and drones, that can make real-time decisions without human intervention.
6. Robotics: AI-driven robots can perform tasks in manufacturing, healthcare, and other industries, increasing efficiency and precision.
7. Healthcare: AI is used in medical diagnosis, drug discovery, personalized treatment plans, and health monitoring.
8. Finance: AI applications in finance include fraud detection, algorithmic trading, credit risk assessment, and customer service chatbots.
9. Gaming and Entertainment: AI enhances gaming experiences through intelligent non-player characters (NPCs) and dynamic game environments.
10. E-commerce: AI powers recommendation engines, personalized shopping experiences, and customer service chatbots in online retail.
11. Cybersecurity: AI is utilized to detect and prevent cyber threats, identify suspicious behavior, and enhance network security.
12. Education: AI can be used for personalized learning, intelligent tutoring systems, and automated grading.
13. Climate Prediction: AI helps analyze climate data to predict weather patterns and assess the impact of climate change.
14. Human Resources: AI streamlines the recruitment process, automates resume screening, and provides data-driven insights for talent management.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of AI, and the field continues to evolve rapidly, opening up new possibilities and opportunities across industries.
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data Science
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Data Science are related concepts, but they are not the same thing. Here’s the difference between them:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is a broader field of computer science that aims to create intelligent machines or systems that can simulate human intelligence.AI aims to create robots that are capable of learning, thinking, solving problems, perceiving, and interpreting language—tasks that traditionally require human intelligence.AI encompasses a wide range of techniques and approaches, including machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, expert systems, and more.
In essence, AI is about creating intelligent agents that can mimic human intelligence and make decisions based on data, logic, or experience. It involves building systems that can adapt and improve their performance over time, learning from the data they are exposed to.
2. Machine Learning (ML): Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of relying on explicit instructions, ML algorithms learn from patterns and examples in the data to make predictions or decisions.
ML algorithms are designed to recognize patterns, generalize from past experiences, and make predictions or decisions on new, unseen data. There are various kinds of machine learning, including reinforcement learning, unsupervised learning, and supervised learning, each with unique properties and applications.
3. Data Science: Data Science is an area of study that focuses on obtaining knowledge and insights from data. It combines techniques from statistics, mathematics, computer science, and domain expertise to analyze large and complex datasets. Data scientists collect, clean, and process data, then apply various analytical and statistical methods to derive meaningful information and make data-driven decisions. Data Science includes tasks like data visualization, data mining, predictive modeling, and data-driven decision-making.
In summary:
- AI is the overarching field that seeks to create intelligent machines capable of human-like tasks.
- Data Science is about extracting insights and knowledge from data using statistical and analytical methods.
- Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms allowing machines to learn from data and improve their performance.
Data Science and Machine Learning are key components of AI, as they provide the means to process and understand data and enable machines to learn and make decisions based on that data.
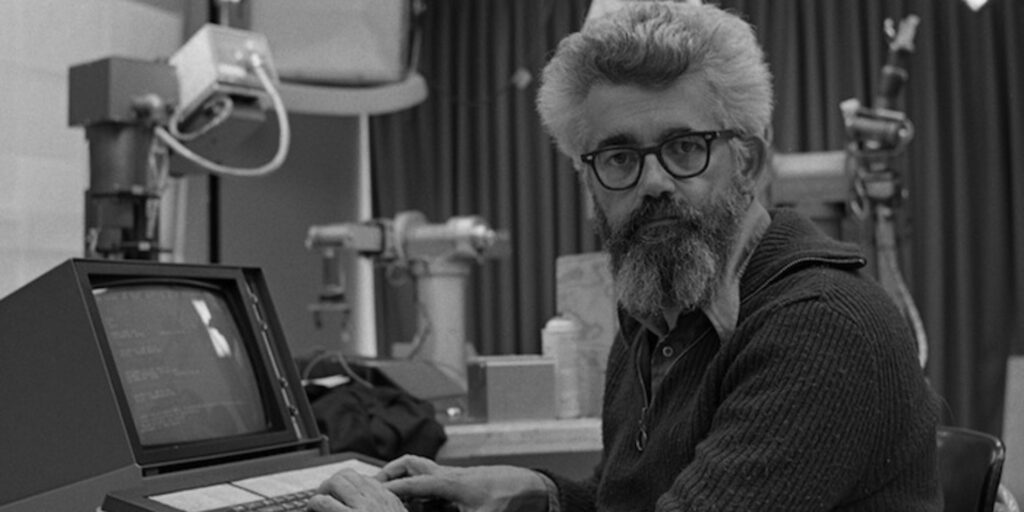

The title “father of artificial intelligence” is often attributed to John McCarthy.John McCarthy was a computer scientist from the United States who made substantial contributions to the field of artificial intelligence. On September 4, 1927, he was born, and on October 24, 2011, he died.McCarthy is best known for coining the term “artificial intelligence” in 1956, during a workshop at Dartmouth College. He organized this workshop, which is widely considered the birth of AI as a scientific discipline.

Informative article